14
Model Tuning
Tidy Data Science with the Tidyverse and Tidymodels
W. Jake Thompson
https://tidyds-2021.wjakethompson.com · https://bit.ly/tidyds-2021
Tidy Data Science with the Tidyverse and Tidymodels is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Your Turn 0
- Open the R Notebook materials/exercises/14-tuning.Rmd
- Run the setup chunk
01:00
KNN
nearest_neighbor()
Specifies a model that uses K Nearest Neighbors
nearest_neighbor(neighbors = 1)nearest_neighbor()
Specifies a model that uses K Nearest Neighbors
nearest_neighbor(neighbors = 1)k = neighbors (PLURAL)
nearest_neighbor()
Specifies a model that uses K Nearest Neighbors
nearest_neighbor(neighbors = 1)k = neighbors (PLURAL)
regression and classification modes
Your Turn 1
Here's a new recipe (also in your .Rmd)...
normalize_rec <- recipe(Sale_Price ~ ., data = ames) %>% step_novel(all_nominal()) %>% step_dummy(all_nominal()) %>% step_zv(all_predictors()) %>% step_center(all_predictors()) %>% step_scale(all_predictors())Your Turn 1
...and a new model. Can you tell what type of model this is?
knn5_spec <- nearest_neighbor(neighbors = 5) %>% set_engine("kknn") %>% set_mode("regression")01:00
Your Turn 1
Combine the recipe and model into a new workflow named knn_wf. Fit the workflow to cv_folds and collect its RMSE.
05:00
knn5_wf <- workflow() %>% add_recipe(normalize_rec) %>% add_model(knn5_spec)knn5_wf %>% fit_resamples(resamples = cv_folds) %>% collect_metrics()#> # A tibble: 2 x 6#> .metric .estimator mean n std_err .config #> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <chr> #> 1 rmse standard 37191. 10 1130. Preprocessor1_Model1#> 2 rsq standard 0.786 10 0.00971 Preprocessor1_Model1Your Turn 2
Repeat the process in Your Turn 1 with a similar workflow that uses neighbors = 10. Does the RMSE change?
05:00
knn10_spec <- nearest_neighbor(neighbors = 10) %>% set_engine("kknn") %>% set_mode("regression")knn10_wf <- knn5_wf %>% update_model(knn10_spec)knn10_wf %>% fit_resamples(resamples = cv_folds) %>% collect_metrics()#> # A tibble: 2 x 6#> .metric .estimator mean n std_err .config #> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <chr> #> 1 rmse standard 35817. 10 972. Preprocessor1_Model1#> 2 rsq standard 0.806 10 0.00869 Preprocessor1_Model1Pop quiz!
How can you find the best value of neighbors/k?
Pop quiz!
How can you find the best value of neighbors/k?
Compare all the separate values/models
tune_grid()
tune()
A placeholder for hyper-parameters to be "tuned"
nearest_neighbor(neighbors = tune())tune_grid()
A version of fit_resamples() that performs a grid search for the best combination of tuned hyper-parameters.
tune_grid( object, resamples, ..., grid = 10, metrics = NULL, control = control_grid())tune_grid()
A version of fit_resamples() that performs a grid search for the best combination of tuned hyper-parameters.
tune_grid( object, resamples, ..., grid = 10, metrics = NULL, control = control_grid())tune_grid()
A version of fit_resamples() that performs a grid search for the best combination of tuned hyper-parameters.
tune_grid( object, resamples, ..., grid = 10, metrics = NULL, control = control_grid())One of:
- a
workflow - a formula
- a
recipe
tune_grid()
A version of fit_resamples() that performs a grid search for the best combination of tuned hyper-parameters.
tune_grid( object, preprocessor, resamples, ..., grid = 10, metrics = NULL, control = control_grid())One of:
- formula +
model recipe+model
tune_grid()
A version of fit_resamples() that performs a grid search for the best combination of tuned hyper-parameters.
tune_grid( object, resamples, ..., grid = 10, metrics = NULL, control = control_grid())One of:
- A positive integer
- A data frame of tuning combinations
tune_grid()
A version of fit_resamples() that performs a grid search for the best combination of tuned hyper-parameters.
tune_grid( object, resamples, ..., grid = 10, metrics = NULL, control = control_grid())Number of candidate parameter sets to be created automatically.
tune_grid()
A version of fit_resamples() that performs a grid search for the best combination of tuned hyper-parameters.
tune_grid( object, resamples, ..., grid = 10, metrics = NULL, control = control_grid())A data frame of tuning combinations.
expand_grid()
Takes one or more vectors, and returns a data frame holding all combinations of their values.
expand_grid(neighbors = c(1,2), foo = 3:5)#> # A tibble: 6 x 2#> neighbors foo#> <dbl> <int>#> 1 1 3#> 2 1 4#> 3 1 5#> 4 2 3#> 5 2 4#> 6 2 5expand_grid()
Takes one or more vectors, and returns a data frame holding all combinations of their values.
expand_grid(neighbors = c(1,2), foo = 3:5)#> # A tibble: 6 x 2#> neighbors foo#> <dbl> <int>#> 1 1 3#> 2 1 4#> 3 1 5#> 4 2 3#> 5 2 4#> 6 2 5tidyr package; see also base expand.grid()
Your Turn 3
Use expand_grid() to create a grid of values for neighbors that spans from 10 to 20. Save the result as k10_20.
02:00
k10_20 <- expand_grid(neighbors = 10:20)k10_20#> # A tibble: 11 x 1#> neighbors#> <int>#> 1 10#> 2 11#> 3 12#> 4 13#> 5 14#> 6 15#> 7 16#> 8 17#> 9 18#> 10 19#> 11 20Your Turn 4
Create a knn workflow that tunes over neighbors and uses your normalize_rec recipe.
Then use tune_grid(), cv_folds and k10_20 to find the best value of neighbors.
Save the output of tune_grid() as knn_results.
05:00
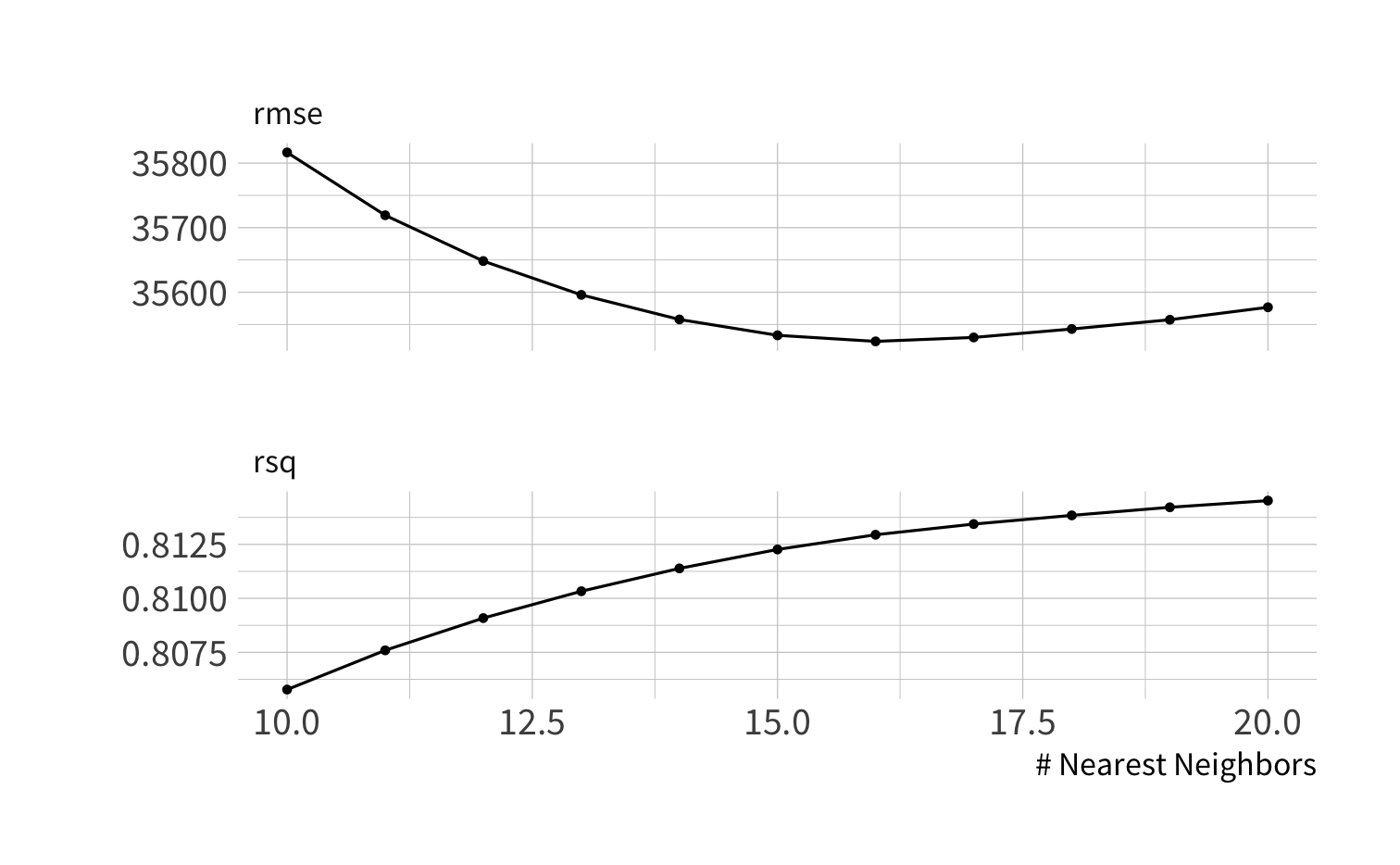
knn_tuner <- nearest_neighbor(neighbors = tune()) %>% set_engine("kknn") %>% set_mode("regression")knn_twf <- workflow() %>% add_recipe(normalize_rec) %>% add_model(knn_tuner)knn_results <- knn_twf %>% tune_grid(resamples = cv_folds, grid = k10_20) knn_results %>% collect_metrics() %>% filter(.metric == "rmse")knn_results %>% collect_metrics() %>% filter(.metric == "rmse")#> # A tibble: 11 x 7#> neighbors .metric .estimator mean n std_err .config #> <int> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <chr> #> 1 10 rmse standard 35817. 10 972. Preprocessor1_Model01#> 2 11 rmse standard 35719. 10 979. Preprocessor1_Model02#> 3 12 rmse standard 35648. 10 991. Preprocessor1_Model03#> 4 13 rmse standard 35596. 10 1004. Preprocessor1_Model04#> 5 14 rmse standard 35558. 10 1017. Preprocessor1_Model05#> 6 15 rmse standard 35533. 10 1030. Preprocessor1_Model06#> 7 16 rmse standard 35524. 10 1044. Preprocessor1_Model07#> 8 17 rmse standard 35530. 10 1057. Preprocessor1_Model08#> 9 18 rmse standard 35543. 10 1068. Preprocessor1_Model09#> 10 19 rmse standard 35557. 10 1078. Preprocessor1_Model10#> 11 20 rmse standard 35577. 10 1088. Preprocessor1_Model11show_best()
Shows the n most optimum combinations of hyper-parameters
knn_results %>% show_best(metric = "rmse", n = 5)show_best()
Shows the n most optimum combinations of hyper-parameters
knn_results %>% show_best(metric = "rmse", n = 5)#> # A tibble: 5 x 7#> neighbors .metric .estimator mean n std_err .config #> <int> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <chr> #> 1 16 rmse standard 35524. 10 1044. Preprocessor1_Model07#> 2 17 rmse standard 35530. 10 1057. Preprocessor1_Model08#> 3 15 rmse standard 35533. 10 1030. Preprocessor1_Model06#> 4 18 rmse standard 35543. 10 1068. Preprocessor1_Model09#> 5 19 rmse standard 35557. 10 1078. Preprocessor1_Model10You can tune models and recipes
Your Turn 5
Modify our PCA workflow provided to find the best value for num_comp on the grid provided. Which is it? Use show_best() to see. Save the output of the fit function as pca_results.
05:00
pca_tuner <- recipe(Sale_Price ~ ., data = ames) %>% step_novel(all_nominal()) %>% step_dummy(all_nominal()) %>% step_zv(all_predictors()) %>% step_center(all_predictors()) %>% step_scale(all_predictors()) %>% step_pca(all_predictors(), num_comp = tune())pca_twf <- workflow() %>% add_recipe(pca_tuner) %>% add_model(lm_spec)nc10_40 <- expand_grid(num_comp = c(10,20,30,40))pca_results <- pca_twf %>% tune_grid(resamples = cv_folds, grid = nc10_40)pca_results %>% show_best(metric = "rmse")#> # A tibble: 4 x 7#> num_comp .metric .estimator mean n std_err .config #> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <chr> #> 1 40 rmse standard 32384. 10 2184. Preprocessor4_Model1#> 2 30 rmse standard 33549. 10 2089. Preprocessor3_Model1#> 3 20 rmse standard 33997. 10 2063. Preprocessor2_Model1#> 4 10 rmse standard 36081. 10 1881. Preprocessor1_Model1library(modeldata)data(stackoverflow)# split the dataset.seed(100) # Important!so_split <- initial_split(stackoverflow, strata = Remote)so_train <- training(so_split)so_test <- testing(so_split)set.seed(100) # Important!so_folds <- vfold_cv(so_train, v = 10, strata = Remote)Your Turn 6
Here's a new recipe (also in your .Rmd)...
so_rec <- recipe(Remote ~ ., data = so_train) %>% step_dummy(all_nominal(), -all_outcomes()) %>% step_lincomb(all_predictors()) %>% step_downsample(Remote)Your Turn 6
...and a new model plus workflow. Can you tell what type of model this is?
rf_spec <- rand_forest() %>% set_engine("ranger") %>% set_mode("classification")rf_wf <- workflow() %>% add_recipe(so_rec) %>% add_model(rf_spec)Your Turn 6
Here is the output from fit_resamples()...
rf_results <- rf_wf %>% fit_resamples(resamples = so_folds, metrics = metric_set(roc_auc))rf_results %>% collect_metrics(summarize = TRUE)#> # A tibble: 1 x 6#> .metric .estimator mean n std_err .config #> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <chr> #> 1 roc_auc binary 0.702 10 0.0151 Preprocessor1_Model1Your Turn 6
Edit the random forest model to tune the mtry and min_n hyper-parameters; call the new model spec rf_tuner.
Update the model for your workflow; save it as rf_twf.
Tune the workflow to so_folds and show the best combination of hyper-parameters to maximize roc_auc.
How does it compare to the average ROC AUC across folds from fit_resamples()?
10:00
rf_tuner <- rand_forest(mtry = tune(), min_n = tune()) %>% set_engine("ranger") %>% set_mode("classification")rf_twf <- rf_wf %>% update_model(rf_tuner)rf_twf_results <- rf_twf %>% tune_grid(resamples = so_folds, metrics = metric_set(roc_auc))#> i Creating pre-processing data to finalize unknown parameter: mtryrf_twf_results %>% collect_metrics()#> # A tibble: 10 x 8#> mtry min_n .metric .estimator mean n std_err .config #> <int> <int> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <chr> #> 1 9 16 roc_auc binary 0.692 10 0.0160 Preprocessor1_Model01#> 2 1 9 roc_auc binary 0.707 10 0.0143 Preprocessor1_Model02#> 3 16 23 roc_auc binary 0.687 10 0.0166 Preprocessor1_Model03#> 4 22 10 roc_auc binary 0.670 10 0.0161 Preprocessor1_Model04#> 5 13 29 roc_auc binary 0.693 10 0.0157 Preprocessor1_Model05#> 6 5 5 roc_auc binary 0.696 10 0.0157 Preprocessor1_Model06#> 7 20 38 roc_auc binary 0.692 10 0.0153 Preprocessor1_Model07#> 8 12 27 roc_auc binary 0.694 10 0.0154 Preprocessor1_Model08#> 9 18 35 roc_auc binary 0.691 10 0.0155 Preprocessor1_Model09#> 10 7 21 roc_auc binary 0.701 10 0.0163 Preprocessor1_Model10defaults:
mtry = sqrt(# predictors) = sqrt(20) = 4
min_n = 1
roc_auc = .702
What next?
show_best()
Shows the n most optimum combinations of hyper-parameters.
rf_twf_results %>% show_best(metric = "roc_auc")#> # A tibble: 5 x 8#> mtry min_n .metric .estimator mean n std_err .config #> <int> <int> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <chr> #> 1 1 9 roc_auc binary 0.707 10 0.0143 Preprocessor1_Model02#> 2 7 21 roc_auc binary 0.701 10 0.0163 Preprocessor1_Model10#> 3 5 5 roc_auc binary 0.696 10 0.0157 Preprocessor1_Model06#> 4 12 27 roc_auc binary 0.694 10 0.0154 Preprocessor1_Model08#> 5 13 29 roc_auc binary 0.693 10 0.0157 Preprocessor1_Model05select_best()
Shows the top combination of hyper-parameters.
so_best <- rf_twf_results %>% select_best(metric = "roc_auc")so_bestselect_best()
Shows the top combination of hyper-parameters.
so_best <- rf_twf_results %>% select_best(metric = "roc_auc")so_best#> # A tibble: 1 x 3#> mtry min_n .config #> <int> <int> <chr> #> 1 1 9 Preprocessor1_Model02finalize_workflow()
Replaces tune() placeholders in a model/recipe/workflow with a set of hyper-parameter values.
so_wfl_final <- rf_twf %>% finalize_workflow(so_best)The test set
Remember me?
fit() and predict()
Remember me?
so_test_results <- so_wfl_final %>% fit(data = so_train)predict(so_test_results, new_data = so_test, type = "class")predict(so_test_results, new_data = so_test, type = "prob")last_fit()
A better way.
so_test_results <- so_wfl_final %>% last_fit(so_split)last_fit()
A better way.
so_test_results <- so_wfl_final %>% last_fit(so_split)#> # Resampling results#> # Manual resampling #> # A tibble: 1 x 6#> splits id .metrics .notes .predictions .workflow#> <list> <chr> <list> <list> <list> <list> #> 1 <split [419… train/tes… <tibble[,4] … <tibble[,1]… <tibble[,6] [1,3… <workflo…Your Turn 7
Use select_best(), finalize_workflow(), and last_fit() to take the best combination of hyper-parameters from rf_results and use them to predict the test set.
How does our actual test ROC AUC compare to our cross-validated estimate?
05:00
so_best <- rf_twf_results %>% select_best(metric = "roc_auc")so_wfl_final <- rf_twf %>% finalize_workflow(so_best)so_test_results <- so_wfl_final %>% last_fit(split = so_split)so_test_results %>% collect_metrics()#> # A tibble: 2 x 4#> .metric .estimator .estimate .config #> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> #> 1 accuracy binary 0.634 Preprocessor1_Model1#> 2 roc_auc binary 0.661 Preprocessor1_Model1Comparing performance
Resampling
#> # A tibble: 1 x 8#> mtry min_n .metric .estimator mean n std_err .config #> <int> <int> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <chr> #> 1 1 9 roc_auc binary 0.707 10 0.0143 Preprocessor1_Model02Comparing performance
Resampling
#> # A tibble: 1 x 8#> mtry min_n .metric .estimator mean n std_err .config #> <int> <int> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <int> <dbl> <chr> #> 1 1 9 roc_auc binary 0.707 10 0.0143 Preprocessor1_Model02Test Set
#> # A tibble: 1 x 4#> .metric .estimator .estimate .config #> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> #> 1 roc_auc binary 0.661 Preprocessor1_Model1Ideally, performance estimated from resampling should be similar to what is seen in the test set. If performance from resampling higher, there may be concerns about overfitting.
final final final
Final metrics
so_test_results %>% collect_metrics()#> # A tibble: 2 x 4#> .metric .estimator .estimate .config #> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr> #> 1 accuracy binary 0.634 Preprocessor1_Model1#> 2 roc_auc binary 0.661 Preprocessor1_Model1Predict the test set
so_test_results %>% collect_predictions()#> # A tibble: 1,397 x 7#> id .pred_Remote `.pred_Not remot… .row .pred_class Remote .config #> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <fct> <fct> <chr> #> 1 train/te… 0.570 0.430 2 Remote Remote Preproces…#> 2 train/te… 0.583 0.417 9 Remote Not re… Preproces…#> 3 train/te… 0.461 0.539 10 Not remote Not re… Preproces…#> 4 train/te… 0.547 0.453 17 Remote Not re… Preproces…#> 5 train/te… 0.627 0.373 23 Remote Not re… Preproces…#> 6 train/te… 0.449 0.551 27 Not remote Not re… Preproces…#> 7 train/te… 0.497 0.503 28 Not remote Not re… Preproces…#> 8 train/te… 0.439 0.561 45 Not remote Not re… Preproces…#> 9 train/te… 0.400 0.600 46 Not remote Not re… Preproces…#> 10 train/te… 0.497 0.503 48 Not remote Not re… Preproces…#> # … with 1,387 more rowsModel Tuning

Tidy Data Science with the Tidyverse and Tidymodels
W. Jake Thompson
https://tidyds-2021.wjakethompson.com · https://bit.ly/tidyds-2021
Tidy Data Science with the Tidyverse and Tidymodels is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.